Center of Modern Control Techniques
and Industrial Informatics
Department of cybernetics and artificial intelligence (DCAI), FEI, Technical University of Košice
Ball & Plate Kyb
 |
Room:
|
Brief model characteristics
- non-linear dynamic MIMO system with two inputs and two outputs
- algorithms of analytical and experimental identification of dynamic systems
- algorithms of the classical (PID/PSD), but also the modern control theory (state optimal control - LQ, model-based predictive control - MPC)
- stabilization of the ball to the required position on the plate
- the reference trajectory tracking
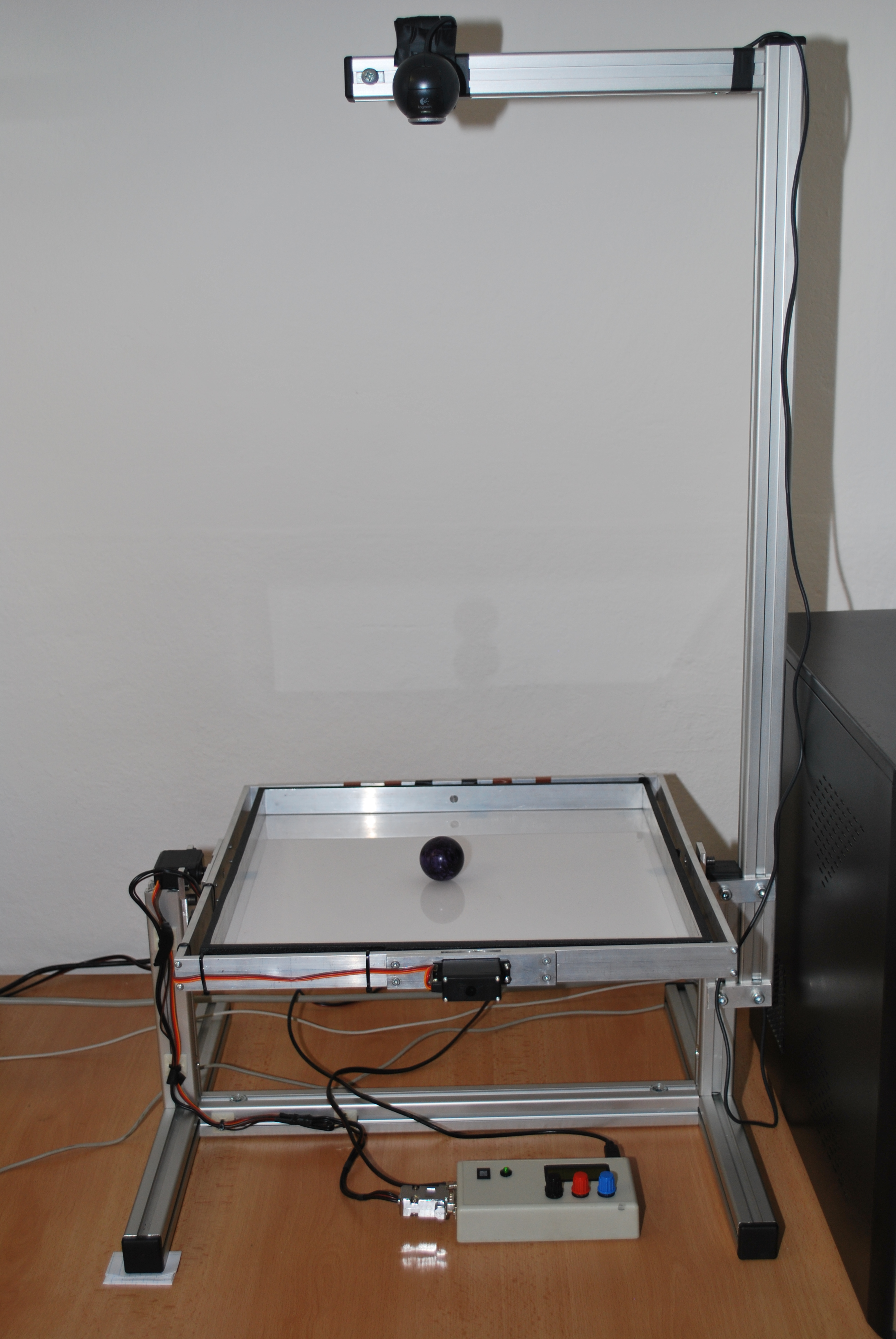
- The experimental workplace consists of the model Ball & Plate B&P_KYB, webcam, the power source of model B&P_KYB, computer with the software Matlab/Simulink and Microcontroller, which provides transmission of signals between computer and real model B&P_KYB through the serial interface RS232. The workplace provides the background for testing wide range of control algorithm.

Obr.1 Experimental workplace
Gallery

|
Model - Mechanical construction
- The model consists the ball and two independent servomotors, which are leaning the plate around its central axis and the webcam, which determines the position of the ball.
- Servomotors are controlled by input signals of the model ux a uy [MU], what influence tipping of plate to the desired position α or β[rad]. The output of the model is captured position of the ball through the webcam. According to captured pictures from webcam and the use of image recognition algorithm the position coordinates of the ball yx a yy are computed.
- Model communicates with computer through the microprocessor using serial interface RS232.
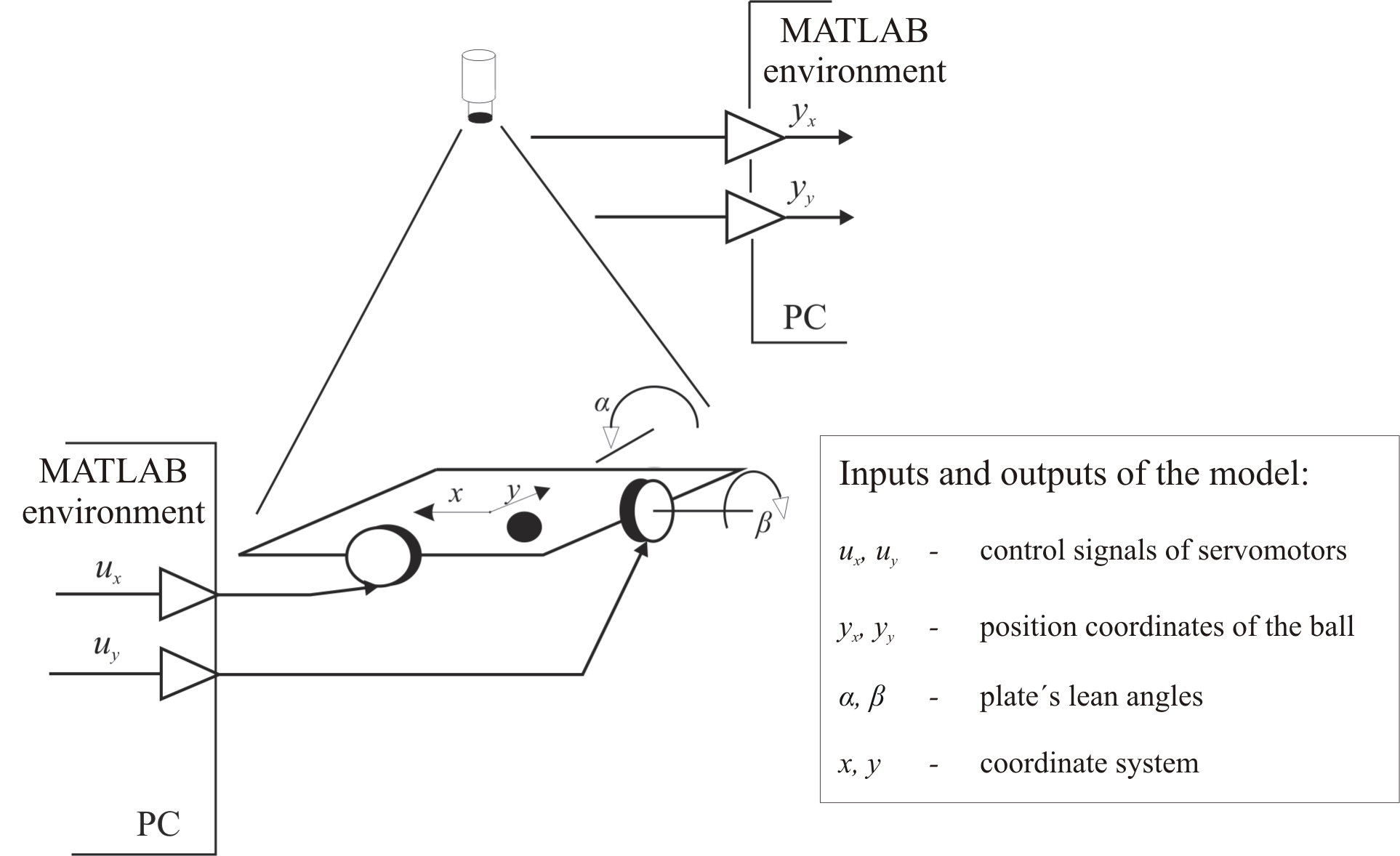
Img.2.: Mechanical construction of the model - scheme
Model - System definition
Control inputs
- input signal ux for servomotor, that lean the plate in x axis
- input signal uy for servomotor, that lean the plate in y axis
Fault inputs
- influence of unmeasurable faults zx, zy,
Measured outputs
- ball's position in x axis: yx [m]
- ball's position in y axis: yy [m]
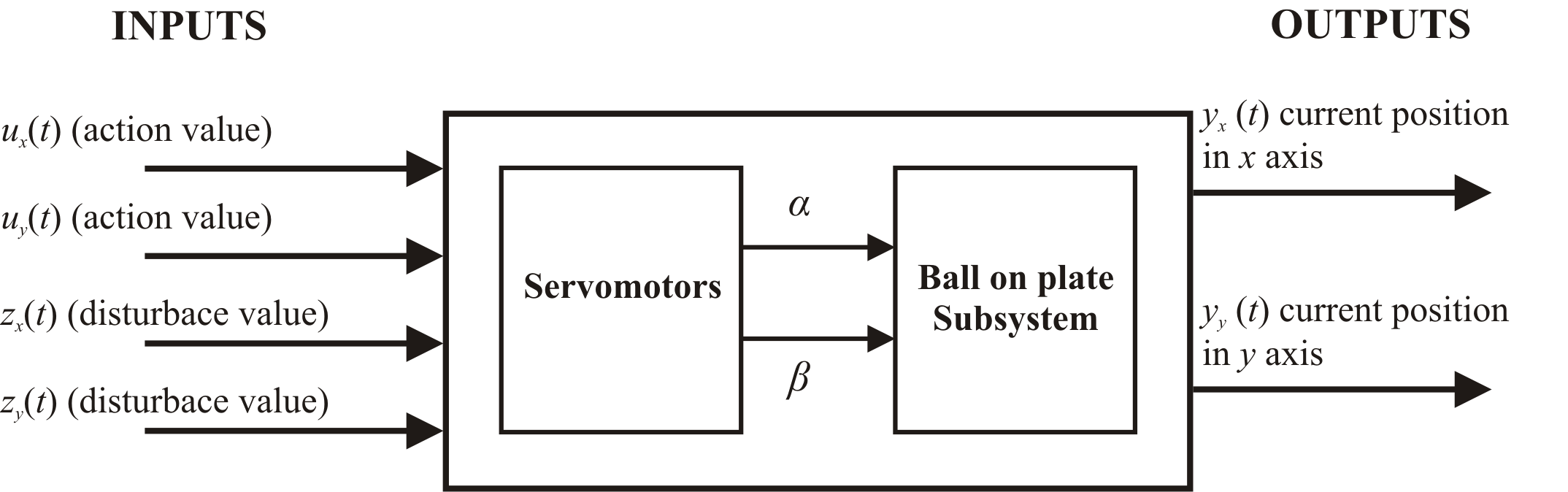
Img.3.: Inputs and outputs of the dynamic model Ball on plate B&P_KYB
Comparison of laboratory models B&P_CE151 (L513) and B&P_KYB (V142)
CE151 |
B&P_KYB |
|---|---|
| -> communication between computer and real model B&P_CE151 through the labcard MF614 | -> communication between computer and real model B&P_KYB through the microprocessor using serial interface RS232 |
| -> the use of functions of REAL TIME TOOLBOX for communication with real model | -> the use of functions of Matlab appointed for communication with the use of the serial interface RS232 |
| -> the use of Image Processing toolbox for image recognition of ball‘s position through the CCD camera | -> Image recognition of ball’s position using OpenCV library through the webcam - Logitech 1.3 MP Webcam C300 |
Using the model in pedagogy
courses
- Simlation systems (2st grade bachelor degree)
- Optimal and Nonlinear systems (1st grade master degree)
- Control and Artificial Intelligence (1st grade master degree)
bachelor thesis
master thesis
-
MATYS, Matúš.: Predictive control of models of physical systems
-
supervisor: doc. Ing. Anna Jadlovská, PhD, consultant: Ing.Štefan Jajčišin.) - 2013
Using the model in research
PhD works
publications
Profile
Infrastructure
Laboratories
Members
Courses
Models
- 32-bit single-chip product
- Flexible Assembly Company
- Ball & Plate CE151
- Ball & Plate B&P_KYB
- Helicopter
- Hydraulic system
- Video camera system
- Crossroad model
- Rotary pendulum
- Magnetic levitation
- Khepera II Mobile robot (simulation approach)
- Motor & frequency converter
- Tracked mobile robot
- Flexible Manufacturing System
- Shelf stacker
- Mitsubishi robot
- SEF robot
- Robot soccer player for MiroSot category
- Robotized workplace
- Light system
- Tensometric (strain) scales
Research
CERN
Gallery
Partners
